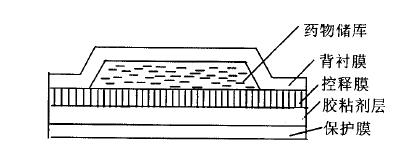
Fig. 1 Warehouse type transdermal system

Fig. 2 Adhesive Dispersed Transdermal System
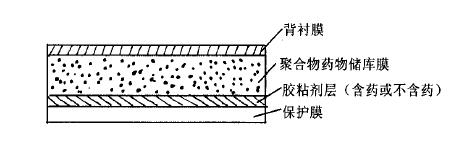
Fig. 3 Transdermal system of polymer drug storehouse
However, for various types of transdermal drug delivery systems, the adhesive layer is the main component, and the pressure-sensitive adhesive is an ideal adhesive for transdermal release, a key auxiliary material of the transdermal drug delivery system, and sometimes it can be used as a drug storage carrier to adjust the drug release rate. For example, pressure-sensitive adhesive in adhesive dispersed transdermal system can not only be used as drug storage carrier, but also regulate drug release rate.
Classification of Pressure Sensitive Adhesives
Pressure sensitive adhesives can be divided into the following categories according to chemical composition:
(1) Rubber type pressure-sensitive adhesive
It can be further divided into natural rubber pressure sensitive adhesive and synthetic rubber pressure sensitive adhesive. Natural rubber pressure-sensitive adhesive, which is the earliest developed rubber type pressure-sensitive adhesive and still has a large output. They are a complex mixture with natural rubber elastomer as the main body and additives such as tackifier, softener, antioxidant, pigment and filler, and crosslinking (vulcanizing) agent. The preparation method of synthetic rubber pressure-sensitive adhesive is similar to that of natural rubber pressure-sensitive adhesive. The main material, natural rubber, can be replaced with synthetic rubber.
(2) Thermoplastic elastomer pressure-sensitive adhesive
Thermoplastic elastomer (TPE), also known as thermoplastic rubber (TPR), is composed of different resin segments and rubber segments with chemical bonds. It has the elasticity of rubber at room temperature and can be plasticized at high temperature, so it is also known as the third generation rubber.
Thermoplastic elastomers represented by styrene butadiene styrene block copolymer (SBS) and styrene isoprene styrene block copolymer (SIS) are the main raw materials for manufacturing hot melt pressure sensitive adhesives.
It can not only form a low viscosity melt at high temperature for preparing hot melt pressure-sensitive adhesive (HMPSA), but also be dissolved in organic solvents to prepare solution pressure-sensitive adhesive, which has been rapidly developed and applied in recent years.
(3) Acrylate pressure-sensitive adhesive
Acrylate pressure-sensitive adhesive is the most widely used pressure-sensitive adhesive at present, and its main body is acrylate copolymer obtained by copolymerization of various acrylate monomers. Due to the wide variety of acrylate monomers, pressure sensitive adhesives that meet different performance requirements can be prepared by using different monomers through copolymerization and crosslinking.
In the past 20 years, acrylate pressure-sensitive adhesive has developed very rapidly and has replaced the dominant position of natural rubber pressure-sensitive adhesive.
(4) Silicone pressure sensitive adhesive
Generally, it refers to the pressure-sensitive adhesive products with organic silicon polymer as the main body and toluene or xylene as the solvent. Compared with the other three traditional pressure-sensitive adhesives, silicon pressure-sensitive adhesives have excellent chemical resistance, water resistance, oil resistance, solvent resistance, high temperature resistance, low temperature resistance, heat resistance, oxidation resistance, degradation and other properties.
In addition, according to the physical morphology of PSA, it can be divided into emulsion type, solvent type, hot melt type, etc.
Common types of pressure-sensitive adhesives in transdermal patches
The adhesion performance of transdermal patches is crucial for transdermal drug delivery. The patches must be in full contact with the skin during the whole delivery process to ensure effective drug delivery. Adhesives used to design transdermal patches mainly include acrylic pressure sensitive adhesive, polyisobutylene silicone pressure sensitive adhesive and hot melt adhesive. Table 1 summarizes the transdermal systems and types of pressure-sensitive adhesives of patches marketed abroad.
Table 1 Some transdermal patches and the use of pressure-sensitive adhesive listed abroad
|
Drug name |
Trade name |
TDDsType |
Pressure sensitive adhesive type |
|
Clonidine |
Catapres-TDDs |
DIA |
Polyisobutylene |
|
Estradiol |
Climara |
DIA |
Polyacrylate |
|
Estradiol |
Estraderm |
Repository type |
Polyisobutylene |
|
Estradiol |
Vivelle |
DIA |
Polyacrylate |
|
Estradiol |
Fempatch |
DIA |
silicon rubber |
|
Fentanyl |
Duragrsic |
Repository type |
Silicon rubber |
|
Nicotine |
Nicoderm |
DIA |
Polyisobutylene |
|
Nicotine |
Harbitrol |
Polymer drug storage |
Polyacrylate |
|
Nicotine |
Nicotrol |
DIA |
Polyisobutylene |
|
Nicotine |
Prostep |
Polymer drug storage |
Polyacrylate |
|
Glyceryl trinitrate |
Transderm-Nitro |
Repository type |
Silicon rubber |
|
Oxibunin |
Oxytrol |
DIA |
Polyacrylate |
|
Slejilan |
Emsam |
DIA |
Polyacrylate |
|
Bunan Selin |
Lonasen |
- |
Polyacrylate |
|
Kabaratine |
Exelon |
Polymer drug storage |
Silicone |
|
Rotigotine |
Neupro |
DIA |
Silicone |
|
Donepezil |
Adlarity |
Repository type |
Polyacrylate |
|
Acenapine |
Secuado |
- |
Hot melt adhesive |
Consideration of Pressure Sensitive Adhesive as Excipient of Transdermal Patch
Pressure sensitive adhesive is the key auxiliary material in the patch, which affects the quality and efficacy of the patch, such as in vitro release test (IVRT), in vitro penetration test (IVPT), adhesion performance and stability.
(1) Effect of Pressure Sensitive Adhesive on IVRT and IVPT
The absorption amount of drugs in transdermal patches depends first on the amount of drugs released from the adhesive matrix. Only drugs reaching the skin surface can enter the systemic circulation through the cuticle and epidermis or skin accessory organs. IVRT can evaluate the rate and extent of drug release from transdermal patches, and is an important indicator in the quality study and stability study. IVPT is to characterize the rate and extent of drug transdermal delivery by simulating the transdermal process of drugs under physiological conditions, in order to partly reflect the quality of drugs and the effectiveness of clinical treatment.
Different types of pressure-sensitive adhesives can exhibit completely different in vitro behaviors due to the great differences in polymer structures. Even for the same type of pressure-sensitive adhesive, the differences in functional groups, additives (such as tackifiers and stabilizers), cross-linking degree and other factors will also lead to significant changes in IVRT and IVPT.
(2) Effect of Pressure Sensitive Adhesive on Adhesion
Transdermal patch is a special dosage form, and the degree and speed of drug release is directly related to the area, tightness and duration of contact between patch and skin. During the whole process of administration, the patch should always be completely and evenly adhered to the skin of the patient, otherwise it may lead to the loss of the delivery amount, thereby reducing the efficacy. Therefore, the adhesive force is an important indicator that affects the use effect of the patch.
In order to achieve the desired adhesion performance of transdermal patches, certain excipients, such as tackifier and plasticizer, are often added to the pressure-sensitive adhesive. Therefore, in the formulation development of transdermal patches, different matrices can be screened or appropriate excipients can be added to meet the adhesion requirements of the patches.
Epilogue
More and more transdermal patches based on pressure-sensitive adhesive technology are being developed. The industrialization of transdermal patches in foreign countries is increasingly mature, while the development and technology of transdermal patches in China are still relatively backward. One of the reasons is the lack of research and development and production of key auxiliary medical pressure-sensitive adhesive.
The query of CDE auxiliary materials registration platform shows that there are 11 medical pressure-sensitive adhesives registered for filing, and domestic enterprises have only one registration number, Jiangsu Kangbeide, and others are imported for filing, including Henkel, DuPont and CosMed Pharmaceuticals of Japan. It can be seen that domestic medical pressure-sensitive adhesives are still insufficient and backward.
Therefore, it can be seen that PSA is a core material and technology in transdermal patches. A key breakthrough in the development of transdermal patches is to vigorously develop the research and development of PSA by local enterprises.
Reference material:
Zhang Xiaohong, Wang Hao, Hou Huimin. Research progress on composition and properties of pressure-sensitive adhesive in transdermal drug delivery system [J]. Chinese Journal of Pharmaceutical Industry, 2008, 39(10):767-772.
WOKOVICH A M, PRODDUTURI S, DOUB W H, et al.Transdermal drug delivery system (TDDS) adhesion asa critical safety, efficacy and quality attribute [J].Eur JPharm Biopharm, 2006, 64(1): 1-8.
LI N, QUAN P, WAN X, et al.Mechanistic insights of theenhancement effect of sorbitan monooleate on olanzapinetransdermal patch both in release and percutaneousabsorption processes [J].Eur J Pharm Sci, 2017, 107: 138-147.
ASSAF S M, SALLAM A S A, GHANEM A M.Design and evaluation of transdermal delivery system containingtamsulosin hydrochloride [J].J Drug Deliv Sci Technol,2019, 51: 524-534.
PURI A, BHATTACCHARJEE S A, ZHANG W, et al.Development of a transdermal delivery system for tenofovir alafenamide, a prodrug of tenofovir with potent antiviral activity against HIV and HBV [J].Pharmaceutics, 2019,11(4): 173.
Note: This article is only for medical, pharmaceutical and other professionals to read.
Some of the pictures are from the network. If there is infringement, please contact to delete.
Lindmik Pharmaceutical(Suzhou)Co.,Ltd is a high-tech pharmaceutical enterprise focusing on the research and development, production and sales of innovative pharmaceutical preparations.Equipped with a number of its own innovative R&D platform of dosage forms, including the transdermal drug delivery system, and at the same time, actively introducing the world’s leading nano-based drug delivery, microspheres drug delivery and other cutting-edge pharmaceutical technologies by means of “license in”, the company is a new rapidly developing company pharmaceutical companies that catches people’s eyes.

12th Floor, Building 5, Tianyun Plaza, 111 Wusongjiang Avenue, Guoxiang Street, Wuzhong District, Suzhou City

0512-66020899

0512-66022699

215124